Big C Discount Drugs Health Information
Gallstones
Pain May Not Be a Symptom
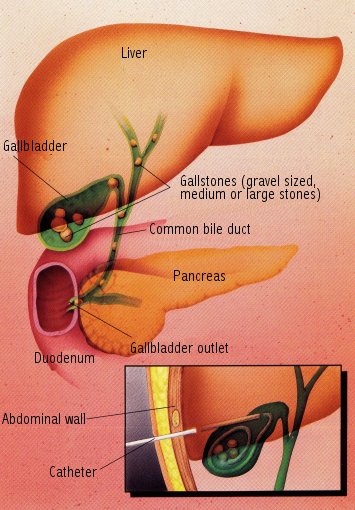
Gallstones are common in middle age and beyond and usually affect overweight women. Severe pain may occur as these stones are pushed out of the gallbladder and into the common bile duct. Therapy consists of surgery or drug therapy. A newer technique is to infuse a drug via a catheter placed directly into the gallbladder over a one- to two-day period to dissolve the stones.Gallstones may be present in the gallbladder for years without causing any problems.
Gallstones Are Common after Age 40
Patients most likely to develop gallstones are women over age 40 who are overweight and have had pregnancies. The risk of gallstones increases with age.Gallstones are formed in the gallbladder, a sac near the liver that receives bile, concentrates it, and sends it to the duodenum through the common bile duct when a meal is eaten. The particles known as "gallstones" are usually made up of cholesterol, but some are calcium salts. Cholesterol is found in bile, and if the bile becomes too saturated with cholesterol, gravel-like stones form in the gallbladder. These particles can be small, medium sized or large. If a stone tries to pass out of the gallbladder, it may move easily into the duodenum, or it may squeeze through the common duct and cause severe pain. If a stone becomes lodged in the common duct, the gallbladder may become inflamed (known as cholecystitis), or the ducts may become infected. A blocked bile duct may also result in jaundice, or a yellowing of the skin, from the backup of bile pigment in the bloodstream.
A gallstone that is blocking the gallbladder outlet, or is trapped in the common duct, causes severe pain in the upper right abdomen that radiates to the shoulder. This pain is steady and continues for hours, usually beginning an hour or so after eating and may even awaken the patient from sleep. It is often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Symptoms: Stones in the gallbladder (cholelithiasis) may cause no symptoms, or the symptoms may not begin until years after they form. There is often tenderness in the upper right abdomen, with a full feeling after a heavy meal, and bloating and belching, especially after eating fried foods. These symptoms, however, can be due to many causes.
Gallstones are most often diagnosed by cholecystography (an x-ray procedure) and ultrasound testing to determine if the gallbladder is functioning, if stones are present, and if they are made of cholesterol or are calcified. If jaundice is present, other tests will be done to determine the cause.
Treatment: In some cases, surgery is indicated to remove the gallbladder. This surgery, called cholecystectomy, eliminates the problem of developing future gallstones. A recently developed drug that dissolves cholesterol gallstones is used in some patients, especially those in whom surgery is a risk. This drug, called chenodiol or CDCA, is effective in dissolving gallstones made of cholesterol (not those that are calcified) when used for 6 to 12 months or up to 24 months. Patients must be monitored carefully during and after their treatment, since over half of all patients treated will develop gallstones again within five years after stopping the drug therapy. Chenodiol must be monitored closely because it may damage the liver. This drug should not be used in women who are pregnant or who could become pregnant. Other drugs with a similar action to chenodiol, but with fewer side effects, are being studied.